Lab tests are an essential part of modern healthcare. They provide valuable information about a person’s health and can help diagnose and monitor various medical conditions. Lab tests involve analyzing samples of blood, urine, or other body fluids or tissues to measure specific substances, markers, or characteristics. Understanding lab test results is crucial for the right diagnosis and making informed decisions about an individual’s health and well-being.
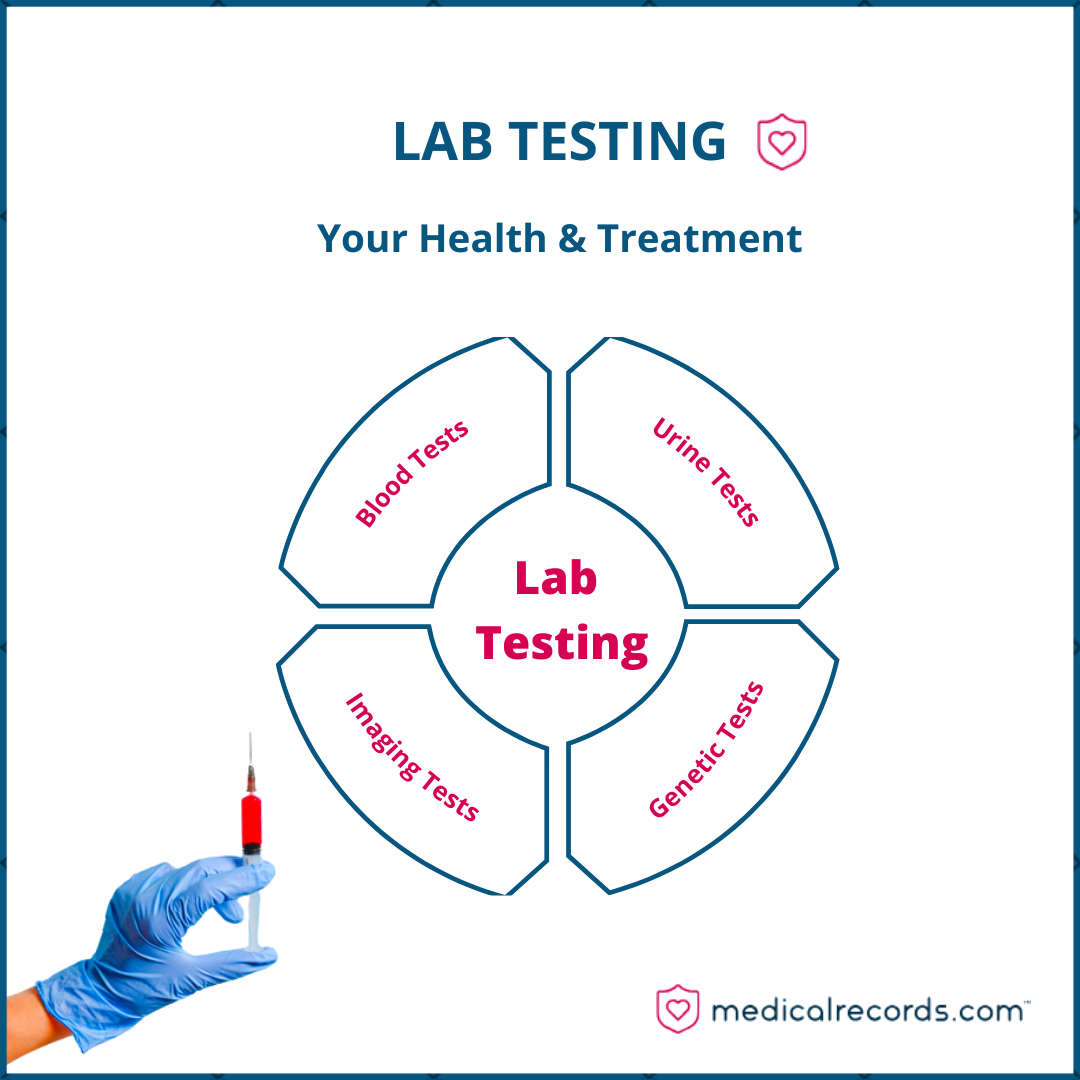
Types of Lab Tests
There are several types of lab tests, each with its own purpose and method of analysis:
- Blood tests: Blood tests are commonly used to detect any diseases and assess the overall health of an individual. These tests analyze blood samples to measure various components, such as blood cells, glucose, cholesterol, and more.
- Urine tests: Urine tests evaluate the chemical composition of urine and can help diagnose kidney and urinary tract disorders, among other conditions.
- Imaging tests: X-rays, MRI, and CT scans are image testing tools that create visual images of the body’s internal structures. These tests are used to detect abnormalities and diagnose diseases.
- Genetic tests: Genetic tests analyze DNA to identify genetic mutations or variations associated with certain diseases or conditions.
Interpreting Lab Test Results
When interpreting lab test results, it’s important to consider the following:
- Normal ranges and abnormal results: Lab tests typically have established normal ranges, which represent the expected values for a healthy individual. Results outside of these ranges may be considered abnormal and could indicate a medical condition.
- Factors that can affect test results: Various factors, such as age, sex, medications, and lifestyle, can influence lab test results. It’s important to discuss these factors with your healthcare provider to interpret your results accurately.
- How to interpret individual test results: Each lab test measures specific markers or substances. Understanding what each test measures and what the results mean is essential for making informed health decisions.
Common Lab Tests and Their Values
Here are some common lab tests and their typical values:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC)
-
-
- Measures the number and types of blood cells
- Values:
- Red blood cell count (4.5 – 5.5 million cells/mcL for men; 4.0 – 5.0 million cells/mcL for women)
- White blood cell count (4,500 – 11,000 cells/mcL)
- Hemoglobin (13.5 – 17.5 grams/deciliter for men; 12.0 – 15.5 grams/deciliter for women)
- Hematocrit (38.8% – 50% for men; 34.9% – 44.5% for women)
- Platelets (150,000 – 450,000/mcL)
-
-
-
- Measures the amount of glucose (sugar) in the blood
- Values:
- Fasting blood glucose (70 – 99 mg/dL)
- 2-hour postprandial glucose (less than 140 mg/dL)
- HbA1c (less than 5.7%)
-
- Lipid Panel
-
-
- Measures cholesterol and triglycerides levels
- Values:
- Total cholesterol (less than 200 mg/dL)
- LDL cholesterol (less than 100 mg/dL)
- HDL cholesterol (greater than 40 mg/dL for men; greater than 50 mg/dL for women)
- Triglycerides (less than 150 mg/dL)
-
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
-
-
- Measures the level of TSH, which stimulates the thyroid gland
- Values:
- TSH (0.4 – 4.0 mIU/L)
-
- Liver Function Tests (LFTs)
-
- Measures liver function and damage
- Values:
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) (less than 40 U/L)
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (less than 40 U/L)
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) (44 – 147 U/L)
- Bilirubin (less than 1.2 mg/dL)
- Kidney Function Tests
-
-
- Measures kidney function and damage
- Values:
- Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) (6 – 20 mg/dL)
- Creatinine (0.6 – 1.3 mg/dL)
-
- C-reactive Protein (CRP)
-
- Measures inflammation in the body
- Values:
- CRP (less than 1 mg/L)
Next Steps After Receiving Lab Test Results
Once you receive your lab test results, it’s important to take the following steps:
- Follow-up testing or consultations with a healthcare professional: If your lab test results are abnormal or if you have questions about your results, it’s important to schedule a follow-up appointment with your healthcare provider. They can help you understand the results and determine if additional testing is needed.
- Lifestyle changes to improve lab test results: Depending on your lab test results, your healthcare provider may recommend lifestyle changes to improve your health. Dietary changes, exercise routines, stress management techniques, and proper sleep are examples of such lifestyle changes.
Conclusion
In summary, lab tests are a vital tool in modern healthcare, providing valuable insights into a person’s health status. There are various types of lab tests, including blood tests, urine tests, imaging tests, and genetic tests, each serving a specific purpose. When interpreting lab test results, it’s essential to understand normal ranges, factors that can affect results, and the significance of individual tests.
Some common lab tests include the Complete Blood Count (CBC), Blood Glucose test, Lipid Panel, Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) test, Liver Function Tests (LFTs), Kidney Function Tests, and C-reactive Protein (CRP) test. Each test measures specific markers or substances, and understanding the typical values for each test is crucial.
After receiving lab test results, it’s important to follow up with a healthcare professional for further interpretation and guidance. Lifestyle changes may also be recommended to improve your health.
Remember that interpreting lab test results can be complex and may require the expertise of a healthcare professional. It’s always a good idea to discuss your results with your healthcare provider to obtain personalized guidance on what the results mean for you and any necessary next steps. Regular lab testing is an important part of maintaining good health and staying proactive about your well-being.