Infertility is a widespread issue that affects many loving couples and their dreams of starting a family. Approximately one in eight couples trying to conceive face this challenge. It is defined as the inability to achieve pregnancy after one year of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse for women under 35, and after six months for women 35 and older. Unexplained infertility can be a deeply emotional experience. However, the journey through infertility can also be one of hope and optimism, as advancements in medical testing and treatment options are making it possible for more couples to overcome fertility barriers and achieve a healthy pregnancy.
Initial Evaluation
The first step in evaluating infertility involves a caring and thorough review of the couple’s medical history and physical examination. Fertility specialists understand the sensitive nature of this issue and strive to create a supportive and friendly environment.
This process includes:
- Infertility Evaluation through an assessment of lifestyle factors: Being overweight, smoking, and stress levels can adversely impact fertility. A physical examination and addressing these factors through lifestyle changes, medication, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can improve the chances of conception.
- Evaluation of previous medical conditions: Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders can affect fertility. Depression can also impact fertility, as it can disrupt hormone levels and decrease the frequency of ejaculation.
- Exploration of family history: Genetic factors, including testosterone levels and genetic disorders, may contribute to infertility. Genetic testing can help identify chromosomal abnormalities that could affect fertility or the health of a future child.
- Exploring family history is an important part of infertility testing. Genetics can play a role in the ability to conceive and birth a child, as well as the health of any future child. Genetic testing can help identify any chromosomal abnormalities in both partners that may affect fertility or the health of a future child. The genetic tests used for infertility testing often involve analyzing blood samples from both partners to detect any genetic markers that could potentially affect fertility.
- For example, some genetic tests look for mutations in genes associated with disorders like cystic fibrosis or fragile X syndrome that can increase the risk of infertility. Additionally, many genetic tests will also look for genetic markers linked to inherited diseases such as sickle cell anemia or Tay-Sachs disease that could be passed on to any future children.
- Inquiry about menstrual cycles: When it comes to infertility testing, one of the initial questions asked is about a patient’s menstrual cycle. An irregular or absent period can indicate a hormonal imbalance, which could be an underlying factor in difficulties with fertility. If a patient has an irregular menstrual cycle, their doctor may ask questions about the regularity and length of her cycles over the last several months.
- Discussion of sexual history and any previous pregnancies: This information helps create a clearer picture of overall reproductive health and informs the course of infertility treatments.
- Before infertility testing is done, it’s important for both partners to have a candid discussion with their doctor about their sexual history and any previous pregnancies. This information helps doctors create a clearer picture of overall reproductive health and informs the course of testing and treatment.
- A detailed sexual history is an important part of infertility testing. It can provide crucial information that helps healthcare providers determine the best course of action in diagnosing and treating infertility. A thorough sexual history should include questions about a patient’s frequency of intercourse, the timing of unprotected intercourse, any contraceptive use, pregnancy history, prior sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and any past fertility issues.
During this phase, doctors will also assess ovulation through a series of blood tests to measure hormone levels. These fertility tests are crucial in determining if a woman is ovulating regularly and producing adequate levels of hormones necessary for conception. Understanding a woman’s menstrual cycle and its relation to ovulation is essential to increase the chances of fertilizing an egg and achieving pregnancy.
For men, semen analysis is an essential component of the evaluation. It provides insight into potential male fertility issues by assessing sperm count, sperm motility, and sperm morphology, all vital factors in fertilizing an egg.
Another critical test for women is ovarian reserve testing. This evaluation examines the quantity and quality of eggs (“egg supply”) in the ovaries, which can significantly impact the likelihood of conception. Additionally, an ultrasound examination of the uterus and fallopian tubes can identify structural abnormalities that may contribute to infertility, such as fibroids, polyps, or blockages.
Additional Testing for Women
In some cases, further testing may be required to pinpoint the cause of female infertility.
These tests include:
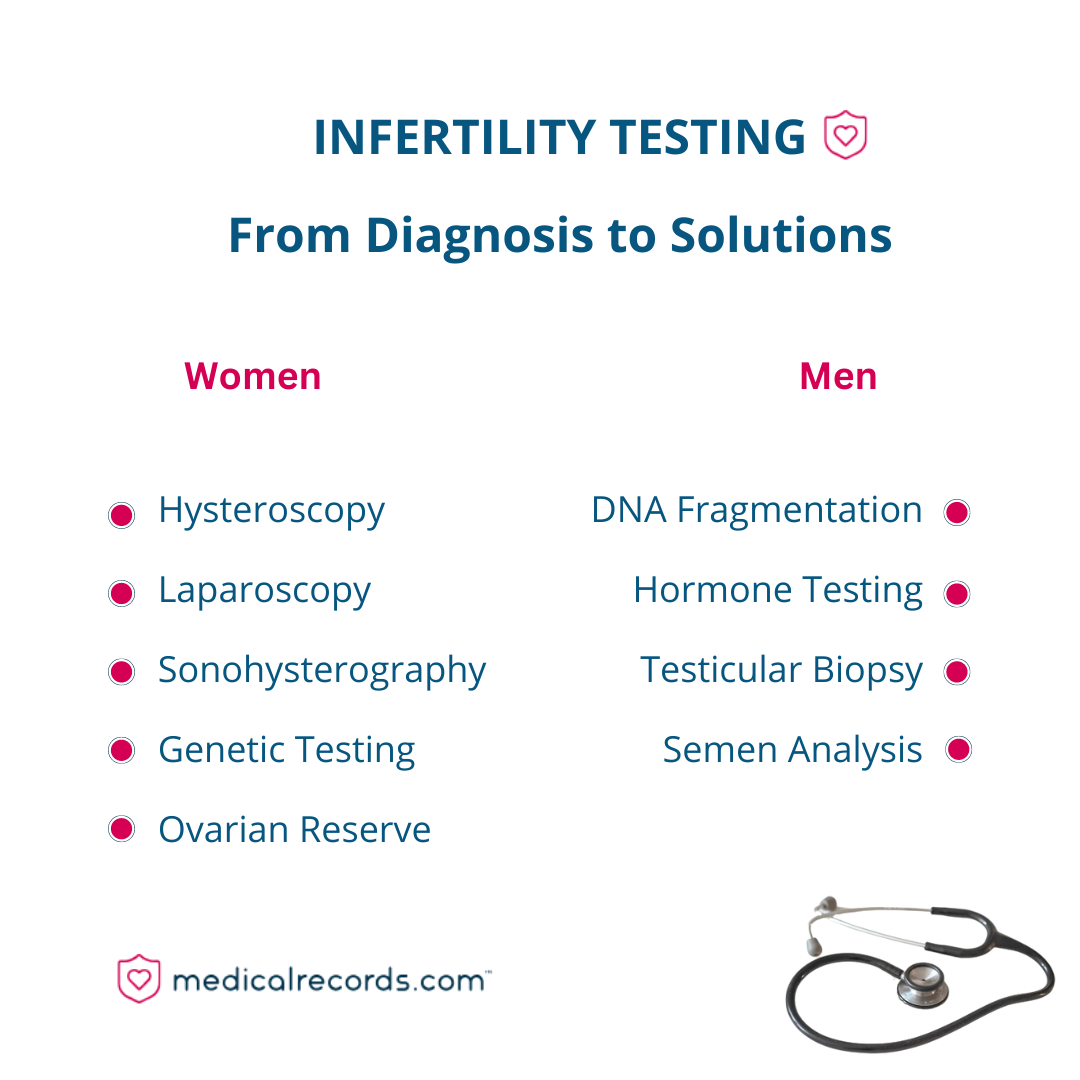
- Hysteroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure that involves inserting a thin, lighted scope into the uterus to examine its lining for abnormalities. This can help detect issues such as scarring, polyps, or fibroids that may be impacting fertility. The friendly and skilled medical professionals performing this procedure will ensure the utmost comfort and care during the process.
- Laparoscopy: A surgical procedure that evaluates the pelvic region, including the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and uterus, to identify and potentially treat issues such as endometriosis, adhesions, or blocked fallopian tubes. A laparoscopy allows doctors to address these issues in a precise and targeted manner, increasing the chances of a successful pregnancy.
- Sonohysterography: A non-invasive procedure that combines ultrasound imaging with a saline solution to provide a detailed view of the uterine cavity. This innovative method allows doctors to identify abnormalities not visible through traditional ultrasound techniques, offering a more comprehensive understanding of potential fertility issues
- Genetic testing: For women with a family history of genetic disorders or recurrent miscarriages, genetic testing can provide valuable information about their reproductive health. This testing examines chromosomes to identify potential issues that may impact fertility or the health of a future child.
Additional Testing for Men
Men may also undergo further testing (along with a physical examination) to better understand the cause of their fertility issues, including:
- DNA fragmentation testing: Evaluates the integrity of sperm DNA, which can be an indicator of reduced fertility potential. High levels of DNA fragmentation (Sperm DNA damage) have been linked to lower success rates with assisted reproductive technologies, such as in-vitro fertilization (IVF).
- Hormone testing: Measures imbalances in hormones such as testosterone, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH) that can impact sperm production. By identifying and addressing any hormonal imbalances, men can improve their chances of contributing to a successful pregnancy.
- Testicular biopsy: Assesses the presence and quality of sperm within the testicles, particularly in cases of azoospermia (no sperm in the ejaculate). Testicular tissue may be biopsied to determine if a genetic disorder is causing the absence of sperm. While the idea of a testicular biopsy might sound daunting, rest assured that experienced healthcare professionals will take every precaution to ensure the patient’s comfort and safety during the procedure.
Special Cases
Individuals with specific medical histories may require specialized testing in the treatment of infertility, including:
- Women with a history of recurrent miscarriage: Testing to identify potential causes, such as chromosomal abnormalities, hormonal imbalances, or autoimmune disorders. It is crucial to understand that experiencing recurrent miscarriages can be an emotionally draining experience, and the medical professionals involved will provide compassionate care and support throughout the testing process.
- Women with a history of ectopic pregnancy: Additional evaluation to assess the health of their fallopian tubes and identify any underlying risk factors. Early detection of these issues can lead to more targeted treatment options, increasing the likelihood of a healthy pregnancy.
- Men with a history of undescended testicles: Specialized testing, including hormonal testing, ultrasound examinations, and potentially testicular biopsy to assess sperm production. This targeted approach can help pinpoint any fertility issues associated with undescended testicles and offer appropriate treatment options.
Conclusion
If you and your partner are struggling with infertility, it’s essential to seek help from a fertility specialist. Remember that you are not alone in this journey. A supportive network of doctors, nurses, and other healthcare providers is ready to help you navigate the complex world of infertility testing and treatment. Advances in diagnostics and treatments offer hope to infertile couples, allowing many to realize their dreams of growing their family.
Once testing is complete, various treatments for infertility options may be available, such as fertility medications, intrauterine insemination (IUI), or in-vitro fertilization (IVF). Each of these treatments is designed to support and enhance your chances of conceiving. Your healthcare team will work closely with you to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your unique needs and circumstances.
It’s essential to maintain a positive outlook throughout this journey, as emotional well-being can impact fertility. Seek support from friends, family, or support groups, and consider speaking with a therapist if feelings of depression or anxiety arise.
While some fertility treatments may carry risks, such as surgical complications, premature birth, or bleeding, your healthcare team will closely monitor your progress and work to minimize any potential risks. By staying informed, working closely with your fertility specialist team, and maintaining a positive attitude, you can increase your chances of overcoming infertility and welcoming a new member to your family.
FAQ
Can my OBGYN test for infertility?
Yes, your OBGYN can test for infertility. Obstetricians and gynecologists are trained to diagnose and treat various reproductive issues, including infertility. They may perform a series of tests, such as blood tests, ultrasound, and pelvic exams, to determine the cause of infertility and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Can a gynecologist test for infertility?
Yes, a gynecologist can test for infertility. Gynecologists specialize in the female reproductive system and are well-equipped to diagnose and treat fertility issues. They may perform various tests, such as hormone level assessments, imaging studies, and laparoscopic examinations, to identify potential causes of infertility.
Does insurance cover infertility testing?
Insurance coverage for infertility testing varies depending on your specific insurance plan and the laws in your state. Some plans cover infertility testing, while others only cover certain tests or treatments. It is essential to check with your insurance provider to understand the extent of coverage for infertility testing and treatments.
How much does it cost to get tested for infertility?
The cost of infertility testing varies depending on the specific tests required and your location. On average, basic fertility testing can cost between $100 and $500. However, more comprehensive testing and specialized procedures can cost several thousand dollars. It is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate tests and discuss potential costs.
Where can I get an infertility test?
Infertility testing can be done at various locations, such as:
- OBGYN or gynecologist’s office
- Fertility clinics
- Reproductive endocrinologist’s office
It is essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best place for your specific needs.
When to get tested for infertility?
It is recommended to seek infertility testing if:
- You are under 35 and have been trying to conceive for over a year without success
- You are over 35 and have been trying to conceive for six months without success
- You have irregular menstrual cycles or a history of reproductive issues
Can a smear test detect infertility?
A smear test, also known as a Pap smear or cervical screening, is designed to detect abnormal cells in the cervix, which can lead to cervical cancer. It cannot directly detect infertility. However, if your healthcare provider suspects an issue during a smear test, they may recommend additional testing for infertility.
Can blood tests detect infertility?
Blood tests can be used to assess hormone levels, which can provide valuable information about fertility. For instance, tests can measure levels of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), prolactin, and anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH), among others. These hormone levels can help determine if there are any hormonal imbalances that may be contributing to infertility.
Can ovulation tests show infertility?
Ovulation tests can help determine if a woman is ovulating regularly, which is crucial for fertility. However, these tests cannot diagnose infertility on their own. If ovulation tests consistently indicate that ovulation is not occurring, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Are fertility tests painful?
Fertility tests can range from non-invasive blood tests to more invasive procedures like hysterosalpingography (HSG) or laparoscopy. While blood tests and ultrasound are generally painless, some tests, such as HSG or laparoscopy, can cause discomfort or mild pain. Your healthcare provider will discuss any potential discomfort and pain management options with you during the testing process.
Can small testes cause infertility?
Small testes can be a cause of infertility in men, as they may produce fewer sperm or lower-quality sperm. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if small testes are indeed the cause of infertility and to explore potential treatment options.
How do men get tested for infertility?
Men can undergo several tests to evaluate their fertility, including:
- Semen analysis: This test evaluates sperm count, motility, and morphology to determine overall sperm health.
- Blood tests: These tests can measure hormone levels, such as testosterone, which can impact fertility.
- Physical examination: A healthcare provider may examine the genitals for any abnormalities or signs of infection that could affect fertility.
- Imaging studies: Ultrasound or MRI can help identify structural issues, such as varicoceles or obstructions in the reproductive system.
How to test if a woman is infertile at home?
At-home testing options for women are limited and cannot provide a comprehensive evaluation of fertility. Ovulation predictor kits can help track ovulation and identify potential issues with the ovulation process. However, if you suspect fertility issues, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider for a more thorough assessment.
What test would tell if a woman is infertile and its cost?
Several tests can help determine if a woman is infertile, including blood tests, imaging studies, and more invasive procedures. The cost of these tests varies depending on the specific test and location. Basic fertility tests can range from $100 to $500, while more comprehensive tests and procedures can cost several thousand dollars.
How early can you tell if you’re infertile?
Infertility can be difficult to predict, as many factors can contribute to fertility issues. Generally, it is recommended to seek infertility testing if you have been trying to conceive for over a year (if under 35) or six months (if over 35) without success. However, if you have a history of reproductive issues or irregular menstrual cycles, it may be beneficial to consult with a healthcare provider sooner.
When should you suspect infertility?
You should suspect infertility if:
- You are under 35 and have been trying to conceive for over a year without success
- You are over 35 and have been trying to conceive for six months without success
- You have irregular menstrual cycles or a history of reproductive issues
What are 3 ways to prevent infertility?
To help prevent infertility, consider the following:
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight can promote fertility.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption: Both smoking and excessive alcohol use can negatively impact fertility.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can negatively affect hormone levels and overall fertility. Practicing stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help support overall well-being and fertility.
What should you not do before a fertility test?
Before a fertility test, you should avoid:
- Smoking or consuming excessive amounts of alcohol
- Taking certain medications that may affect hormone levels or test results (consult your healthcare provider)
- Engaging in sexual intercourse (for semen analysis) for 2-5 days before the test
What is the 21-day test for fertility?
The 21-day test, also known as the progesterone test, is a blood test that measures the level of progesterone in a woman’s blood. It is typically performed on day 21 of the menstrual cycle, assuming a regular 28-day cycle. This test can help determine if a woman is ovulating regularly and producing sufficient progesterone for a potential pregnancy.
How do I check my egg count for fertility?
An anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) blood test can help estimate a woman’s ovarian reserve or the number of eggs remaining in the ovaries. This test can provide insight into a woman’s fertility potential, but it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider for a comprehensive fertility evaluation.
How can I boost my fertility?
To boost fertility, consider the following:
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight can promote fertility.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption: Both smoking and excessive alcohol use can negatively impact fertility.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can negatively affect hormone levels and overall fertility. Practicing stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help support overall well-being and fertility.
- Monitor your menstrual cycle: Tracking your menstrual cycle can help identify your fertile window and increase your chances of conception.
- Seek medical advice: If you suspect fertility issues, consult with a healthcare provider to address any underlying conditions and receive personalized recommendations.
Cost & Insurance
Are infertility tests covered by insurance?
Insurance coverage for infertility tests varies depending on your specific insurance plan and the laws in your state. Some plans cover infertility testing, while others only cover certain tests or treatments. It is essential to check with your insurance provider to understand the extent of coverage for infertility testing and treatments.
Does insurance cover thyroid testing for infertility?
Insurance coverage for thyroid testing in relation to infertility depends on your specific insurance plan. Since thyroid function can impact fertility, many insurance plans may cover thyroid testing as part of a comprehensive fertility evaluation. However, it is essential to check with your insurance provider for coverage details.
Does Medicaid cover infertility testing?
Medicaid coverage for infertility testing varies by state, as each state has its own specific guidelines and limitations. Some states may cover infertility testing and treatments, while others may not. It is crucial to check with your state’s Medicaid program to determine coverage for infertility testing.
Does insurance cover fertility testing for men?
Insurance coverage for fertility testing in men varies depending on the specific insurance plan and state regulations. Some plans may cover fertility testing for men, while others may have limited coverage or no coverage at all. It is essential to consult with your insurance provider for information on coverage for male fertility testing.
Why doesn’t insurance cover infertility?
Insurance coverage for infertility can be limited for various reasons, such as the high cost of treatments, the complexity of determining the cause of infertility, or the lack of a standardized approach to infertility treatment. Additionally, some insurance companies may classify infertility treatments as elective or non-essential, further limiting coverage. It is crucial to review your insurance policy and consult with your insurance provider to understand the extent of coverage for infertility testing and treatments.
Which states mandate infertility coverage?
As of September 2021, 19 states in the United States have laws that mandate some level of infertility coverage, including Arkansas, California, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Illinois, Louisiana, Maryland, Massachusetts, Montana, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Rhode Island, South Dakota, Texas, Utah, and West Virginia. It is essential to check with your state’s regulations and your insurance provider for up-to-date information on infertility coverage.
Is infertility treatment covered by insurance in the USA?
Insurance coverage for infertility treatment varies by insurance plan and state regulations. Some plans may offer comprehensive coverage for infertility treatments, while others may cover only specific treatments or provide limited coverage. It is essential to consult with your insurance provider to understand the extent of coverage for infertility treatments.
How many cycles of infertility treatment will be covered?
The number of cycles of infertility treatment covered by insurance varies depending on your specific insurance plan and state regulations. Some plans may cover a certain number of cycles, while others may have a lifetime maximum for coverage. It is essential to check with your insurance provider to understand the coverage limits for infertility treatment cycles.
Does my health insurance plan cover fertility treatments?
Coverage for fertility treatments depends on your specific health insurance plan and state regulations. Some plans may cover fertility treatments, while others may provide limited coverage or no coverage at all. It is essential to review your insurance policy and consult with your insurance provider to determine coverage for fertility treatments.
Can You Buy Fertility Insurance?
Fertility insurance, also known as supplemental fertility coverage, can be purchased to help cover the costs of fertility treatments not covered by your primary health insurance. These plans may cover procedures such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), intrauterine insemination (IUI), and other fertility treatments. It is important to research different fertility insurance options and their coverage limitations before purchasing a plan.
Why Is Fertility Treatment Not Covered by Insurance?
Fertility treatment coverage varies by insurance company and plan. Some reasons for limited or no coverage include:
- High cost of treatments: Fertility treatments, especially IVF, can be expensive, leading insurance companies to limit coverage to control costs.
- Elective or non-essential classification: Some insurance companies may classify fertility treatments as elective or non-essential, limiting or denying coverage.
- Lack of standardization: There is no one-size-fits-all approach to fertility treatment, making it difficult for insurance companies to determine coverage criteria.
It is essential to review your insurance policy and consult with your insurance provider to understand the extent of coverage for fertility treatments.